Who We Are
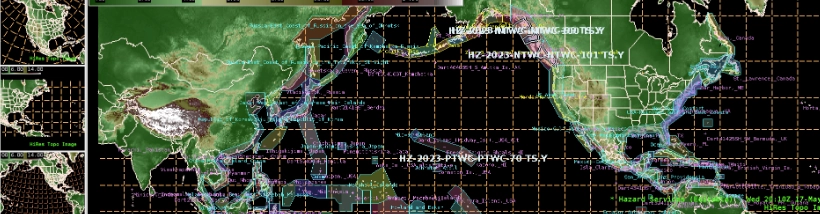
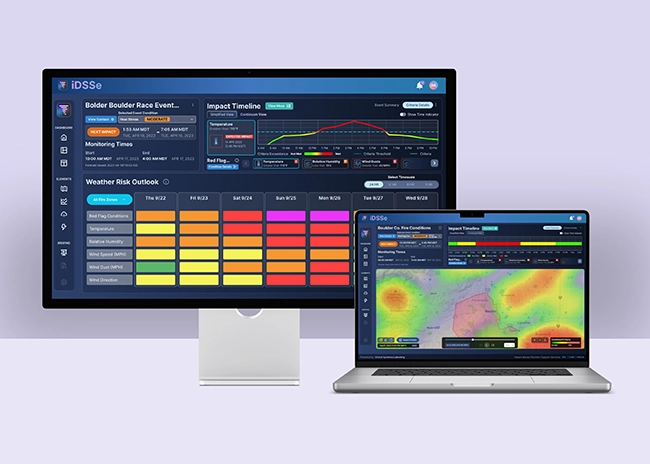
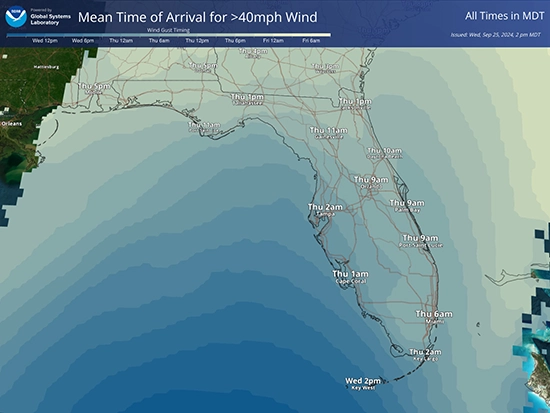
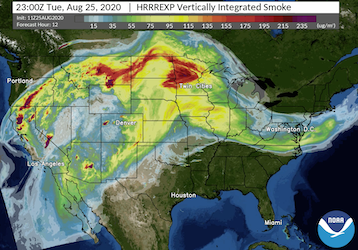
The Weather Informatics and Decision Support (WIDS) Division develops state-of-the-art environmental forecast, warning, decision support, and visualization tools. These capabilities support scientifically robust decision-making processes affected by the weather, water, and atmosphere. We do this by coupling the latest advancements in artificial intelligence, data visualization, social science research, and computer science/engineering with cutting edge atmospheric and environmental science to empower forecasters and decision makers with the best information they need.
WIDS aligns with the GSL Strategic Plan Goal 3: Revolutionize communications, products, and services to enable informed decision-making.
Areas of Research
- Develop applications that improve analysis, visualization, verification, and decision support.
- Research and develop techniques to improve understanding of and effectively communicate weather impacts to our core partners and society at large.
- Ensure investments improve the skill, efficiency, and delivery of products, tools, and applications to operations.
- Research using machine learning and artificial intelligence to enhance and improve the full weather prediction process from data ingest to modeling and decision support.